Networking¶
This page guides you through the available options and helps you decide how to configure your instance's network, depending on your use case.
ScienceCloud implements a networking service that allows you to create complex network setups on the cloud. For basic usage, choose the uzh-only network when creating an instance - your instance will be assigned a UZH-internal IP address.
What you can do with ScienceCloud Networking¶
You have great flexibility when setting up networking. You can:
- Create instances with more than one network interface
- Add or remove a network interface from an instance that is already running
- Assign a public floating IP to an instance
- Create private networks
- Create routers and connect them to private networks
- Switch a floating IP between instances
General non-exhaustive security recommendations¶
Please note that based on the Computing Services Agreement you are not allowed to host services for personal or commercial use, but only for research purposes.
Important
ScienceCloud users bear the sole responsibility for maintaining REIM compliance.
Please note that a new paragraph has been added to the REIM. Section 15 "Schutz des Netzwerks der UZH" (1bis) now stipulates that:
"Sämtliche Logins für vom Internet erreichbare Services, Applikationen und Informatikmittel der UZH müssen über einen zweiten Authentisierungs-Faktor verfügen (Multifaktor-Authentifizierung MFA). Allfällige Ausnahmen sind durch den Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) zu bewilligen".
(Unofficial English translation) All logins for UZH services, applications and IT resources that can be accessed via the Internet must have a second authentication factor (multifactor authentication, MFA). Any exceptions must be approved by the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO).
Entry into force on 5.11.2024. Transition period for implementation of 9 months until 31.7.2025.
- Authenticate exclusively with ssh keys
- Disable password authentication in
sshd_config - Never set passwords for service accounts (
uid < 1000) and accounts withsudoprivileges - Use passphrase-protected ssh keys (these passphrases must be long and unique)
- Configure ssh to use two-factor authentication, e.g.
libpam-google-authenticator
- Disable password authentication in
- Expose only the ports and applications necessary for normal operation
- Never expose your backend databases
- If you need to run an admin or management tool, restrict access to connections coming from UZH IP addresses
- Install security updates regularly
- Enable unattended upgrades
- Follow security bulletins
- Manually upgrade applications that do not originate from the configured package repositories
This is not an exhaustive list and more work may be needed to secure your instance. For more information, refer to the ZI list of IT security recommendations (in particular the REIM) or contact the IT security team. If your server configuration is particularly complex and you need consulting, please contact Science IT to see if an expert service agreement is right for you.
Available Networks¶
By default, there are several pre-configured networks available to ScienceCloud projects: "uzh-only" and "public".
| Name | IP Network | Description | When it should be used... |
|---|---|---|---|
| uzh-only | 172.23.0.0/16 | Private network, routable only within the UZH network | Most computational use cases, when you only need to access your instance to run computational workloads. Also for services that need to be accessed by UZH clients only. |
| External Network VLAN 9 | 10.129.123.0/24 | Public network | For services that need to be contacted from the internet, including public data repositories like OpenBIS or MOOCs (like OpenEdX). You attach an interface from this network to your instance, and then associate a Public Floating IP from the 130.60.9.0/24 network range to it. |
| External Network VLAN 24 | 10.129.192.0/24 | Public network | For services that need to be contacted from the internet, including public data repositories like OpenBIS or MOOCs (like OpenEdX). You attach an interface from this network to your instance, and then associate a Public Floating IP from the 130.60.24.0/24 network range to it. |
| public | 130.60.9.0/24 | Public network | For services that need to be contacted from the internet, including public data repositories like OpenBIS or MOOCs (like OpenEdX). You don't attach your instance directly to this network; instead, you follow the procedure shown for External Network VLAN 9. |
| admin24 | 130.60.24.0/24 | Public network | For services that need to be contacted from the internet, including public data repositories like OpenBIS or MOOCs (like OpenEdX). You don't attach your instance directly to this network; instead, you follow the procedure shown for External Network VLAN 9. |
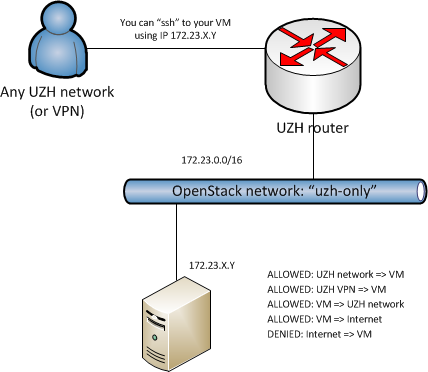
"uzh-only" network¶
This is the standard network for most instances. It contains a range of IP addresses that are only accessible from incoming traffic from inside the UZH network, that is from computers attached to the UZH network either on campus or via VPN. Outgoing traffic from the instance is not limited.
Assigning an internal IP address¶
While launching a new instance, select the Networks page, select the uzh-only network, if not already selected.
Public access to your server¶
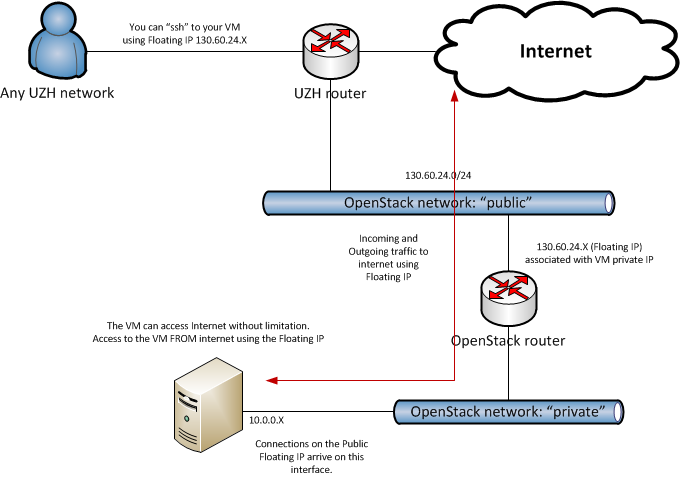
Under certain circumstances, VMs can be made available to the public internet.
Since the UZH public network uses IPv4 and these IPs are intrinsically scarce, the initial quota for the floating IPs on ScienceCloud should only be used when there is a need to serve resources to the public internet. Science IT can provide a limited number of public floating IP addresses for use with web services. However, we strongly recommend that you consider using Web Hosting or Virtual Server Housing services instead. They have higher availability and are better suited for web services than ScienceCloud. If you believe that ScienceCloud is still better suited for your needs, contact Science IT with a description of your use case for a public IP. Once your request is accepted, you will be able to see the available floating IPs from the ScienceCloud dashboard and proceed with the rest of this tutorial.
Note that there is a cost contribution associated with the allocation of each public IP to a project. The reservation uses DHCP, so the IP will be randomly allocated from this range.
Assigning a floating public IP¶
There are two private networks, External Network VLAN 9 and External Network VLAN 24, that are connected to a predefined router with access from the public internet. When creating an instance, choose one of these networks as a first step. To assign a Public Floating IP to an instance, first allocate it to your project, from Network > Floating IPs > Allocate Floating IP by selecting the pool to be public, and then associate the floating IP with the instance's interface to that private network.
Release unused public IPs when not in use¶
This IP range is a scarce resource. Please release them if you no longer need them:
- On the web interface, main page, click on Network on the left menu bar
- Click on the Floating IPs link
- For each floating IP you want to release, from the menu on the right, select Release Floating IP.
Other networks¶
public and admin24 networks are for administrative purposes only. If you need a public floating IP address, see here.
Default security groups¶
The table below lists the default security group created for every new project on ScienceCloud.
| Direction | Ether Type | IP Protocol | Port Range | Remote IP Prefix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egress | IPv4 | Any | Any | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Egress | IPv6 | Any | Any | ::/0 |
| Ingress | IPv4 | Any | Any | - |
| Ingress | IPv4 | ICMP | Any | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Ingress | IPv4 | TCP | 22 (ssh) | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Ingress | IPv6 | Any | Any | - |
For detailed instructions on opening specific ports in the instance, please refer to the Training Handout section training / Access specific ports on your instance.
Special use cases¶
Create a private network¶
Info
These steps are required if you want to create your own private tenant network with a router and associate floating IPs through it. If you only need floating IPs directly from the public network, see here.
- From the web interface select Network from the left menu bar.
- Click on the button + Create Network on the upper-right side.
- On the Network screen, choose a name, for instance, private, then click Next.
- On the Subnet screen, under Network Address, pick an IP range, for instance,
10.65.4.0/24, then click Next. - On the Subnet Details screen, ensure Enable DHCP is selected, then click Create.
Create a router and connect it to the network¶
- In the web interface, select Network from the left column.
- Click + Create Router on the upper-right side.
- Pick a name, for instance, private-router.
- From the External Network menu, select the external provider network (e.g. uzh-only).
- Click Create Router. You should now see the router icon connected to the uzh-only network.
- Move the mouse over the router, and select the + Add Interface button.
- In the Subnet menu, select the private network you created earlier, then click the Add Interface button.
Start an instance with the private network interface¶
- While launching a new instance, from the Networking view, select private as the primary network interface.
- After the instance is created, make a note of the IP allocated to the instance: this will be necessary later.
(Optional) Associate a floating IP¶
- On the main page of the web interface select the Network link on the left column.
- Click the entry Floating IPs.
- If you do not yet have an IP listed, click the button Allocate IP to Project.
- Click Allocate IP. An IP should now appear in the list.
- Once an IP is available on the IP Address menu, select the button Associate.
- Ensure the Port to be associated contains the instance name and the correct private IP for the instance as noted in the earlier step.
- Click on the Associate button.
Remember to update the security groups to open the ports needed to connect to your instance with protocols other than SSH.
Public IP migration from the legacy ScienceCloud¶
It is possible to have public IPs that are used in the legacy ScienceCloud migrated to the current ScienceCloud along with a project's related resources when this is required. In this case, the requirement needs to be clarified before the migration process is started.
In this case, the IP address will be deactivated on the legacy ScienceCloud and allocated to the project in the current ScienceCloud. In this case, the IP will belong not to the "public" network, but to the "External Network VLAN 24" network. Once the IP has been migrated to your project, you will be notified and the IP will be available for use. To use it, the steps are similar to those above:
- While launching a new instance, click on the
Networkingtab - Select
External Network VLAN 24as primary interface (assigned toNIC:1) - Make a note of the IP allocated to the instance: this will be necessary later.
After the instance is created, you can associate the public IP address:
- On the web interface, main page, click on the
Networklink - Click on the
Floating IPslink - For the IP you wish to use, click the
Associatebutton on the right of the IP's row - Make sure the IP Address is correct in the first field.
- Ensure the
Port to be associatedcontains the instance name and the correct IP belonging to the correct network and IP for the relevant instance, as noted in the earlier step. - Click on the
Associatebutton
Advanced networking¶
This is the best option if:
- You want to replicate an existing complex network setup for testing purposes
- You need to deploy a distributed service composed of multiple VMs with different roles and needs in terms of network configuration
You have the ability to create private networks and routers and connect them as you wish. However, since multiple configurations are possible, and this use case is less common, we do not describe it here in detail.
If you need assistance with setting up your network configuration, please contact Science IT.